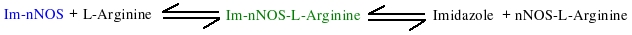| Name | L-Arginine |
| Accession Type | Pathway |
| Transcriber | Sharat J. Vayttaden and Prasoon Agarwal, NCBS |
| Developer | Abu-Soud HM, Wang J, Rousseau DL, and Stuehr DJ |
| Entry Date (YYYY-MM-DD) | 2006-08-07 00:00:00 |
| Species | Human |
| Tissue | Kidney cell expressing the rat brain nNOS |
| Cell Compartment | Cytosol |
| Source | Abu-Soud HM et al. Biochemistry. 1999 Sep 21;38(38):12446-51. ( Peer-reviewed publication ) |
| Methodology | Quantitative match to experiments |
| Model Implementation | Exact GENESIS implementation |
| Model Validation | Approximates original data |
| Notes | This model was taken from the Abu-Soud HM et al. Biochemistry. 1999 Sep 21;38(38):12446-51. This model shows kinetic binding of L-Arginine to neuronal nitric oxide synthase.
Model shows the substrate (L-Arginine) binding to nNOS in a two-step reversible fashion. First there is rapid binding equilibrium between Im-nNOS and L-Arginine to form an intermediate that contains bound imidazole and L-Arginine. This is followed by a slower conformational change in the Im-enzyme-substrate complex that is associated with release of bound imidazole and generation of a modified enzyme-substrate complex which is detected due to spectral change. Replicates Figure 4 (right panel).
|